
Poly(A) + RNA was isolated from various developmental stages of embryos, larvae, pupae, and adult flies (Canton-S) using a μMACS RNA isolation kit (PerkinElmer Life Sciences). DJNK and Hep were cloned into pGEX-4T-1 (AmershamBiosciences) at SmaI/ XhoI and EcoRI/ XhoI sites, respectively, to produce GST fusion proteins. Hep and DKLC cDNA were inserted into pcDNA3 at EcoRI/ XhoI with a FLAG tag at the amino terminus. APPL cDNA was inserted into pcDNA3 at EcoRI/ XbaI. Full-length cDNAs of Drosophila APPL (GenBank J04516), Drosophila JNK (DJNK GenBank U49249), and Drosophila hemipterous (Hep GenBank U93032), and a partial cDNA encoding amino acids 162–508 of the Drosophila kinesin light chain (DKLC GenBank L11013) were obtained by RT-PCR from poly(A) + RNA of 12–18-h embryos. cDNAs of APLIP1, NΔ207, and CΔ137 were cloned into the mammalian expression vector pcDNA3.1Myc/HisA (Invitrogen) to produce pcDNA3.1APLIP1Myc/HisA, pcDNA3.1APLIP1-NΔ207Myc/HisA, and pcDNA3.1APLIP1-CΔ137Myc/HisA, respectively these constructs express proteins tagged with a c-Myc epitope at the carboxyl terminus in mammalian cells. The cDNA encoding the full-length APLIP1 protein (APLIP1) and the PCR-produced carboxyl-terminal deletion construct CΔ137 (amino acids 1–353) were cloned into pGAD424 (Clontech) at SmaI/ PstI sites. cDNAs encoding APPLcyt(834–886) and APPLcytΔ873–882 were inserted into a pGEX-4T-1 vector (Amersham Biosciences) at EcoRI/ SalI sites to produce GST fusion proteins. ) was cloned into pGBT9 (Clontech) at EcoRI/ BamHI sites for yeast two-hybrid screening.
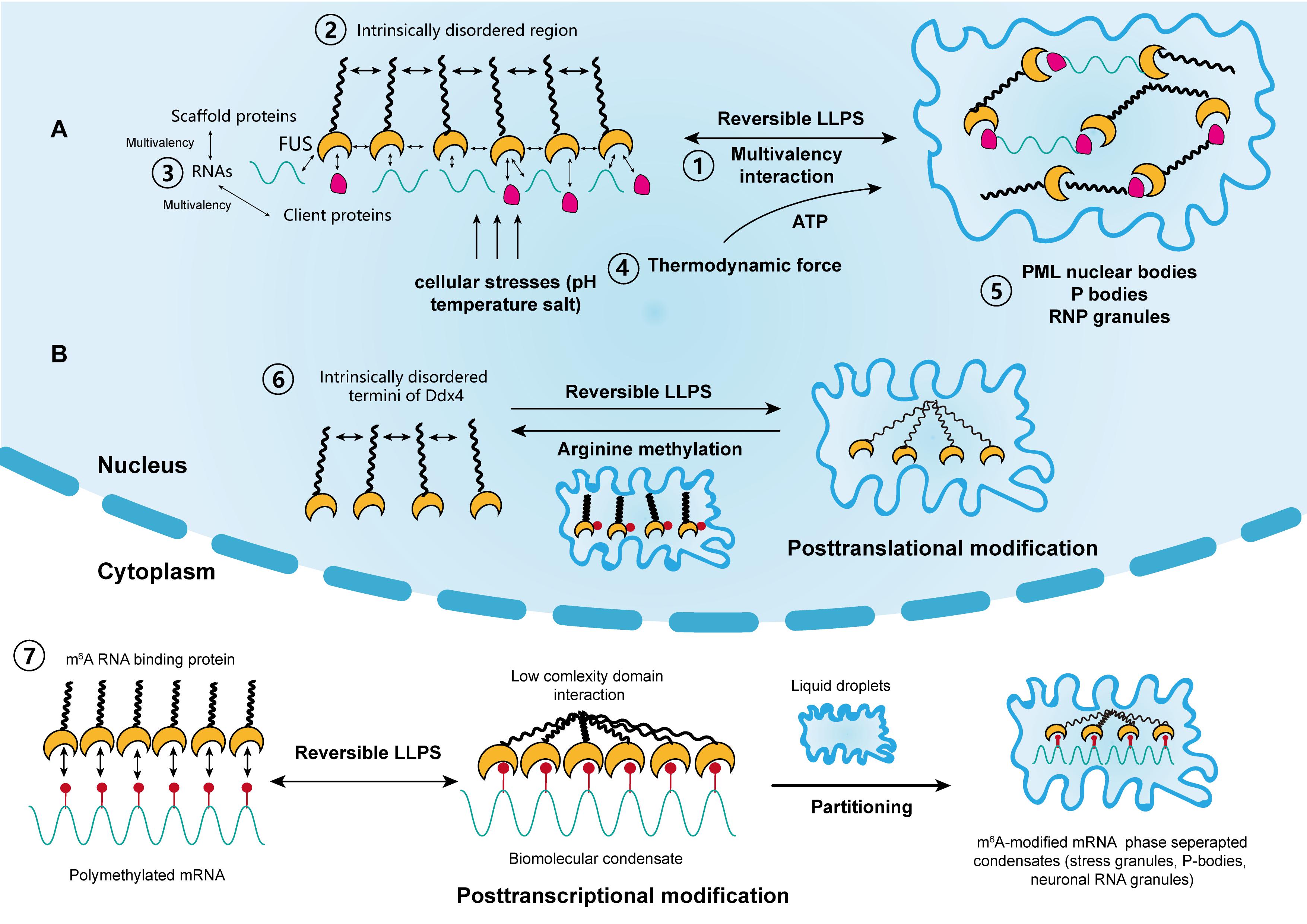
Analysis of APP family proteins and their associated proteins is expected to contribute to understanding the molecular process of neural degeneration in Alzheimer's disease. These observations suggest that the interactions of APP family proteins with APLIP1, JIP1b, and JIP2 are conserved and play important roles in the metabolism and/or the function of APPs including the regulation of APP phosphorylation by JNK. Overexpression of JIP1b slightly enhances the JNK-dependent threonine phosphorylation of APP in cultured cells, but that of JIP2 suppresses it. JIP1b interacts strongly with the cytoplasmic domain of APP (APPcyt), as APLIP1 does with APPL, but the interaction of JIP2 with APPcyt is weak. The similarity of APLIP1 to JIP1b and JIP2 includes interaction with component(s) of the JNK signaling pathway and with the motor protein kinesin and the formation of homo-oligomers. APLIP1 is highly homologous to the carboxyl-terminal halves of mammalian c-Jun NH 2-terminal kinase (JNK)-interacting protein 1b (JIP1b) and 2 (JIP2), which also contain Src homology 3 and phosphotyrosine interaction domains. The phosphotyrosine interaction domain of APLIP1 interacts with a sequence containing GYENPTY in the cytoplasmic domain of APPL. This novel APP L- interacting protein 1 (APLIP1) contains a Src homology 3 domain and a phosphotyrosine interaction domain and is expressed abundantly in neural tissues. We have isolated a novel protein based on its association with Drosophila APP-like protein (APPL), a homolog of the β-amyloid precursor protein (APP) that is implicated in Alzheimer's disease. Glycobiology and Extracellular Matrices.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
